What’s Changed: 2019 Gartner Magic Quadrant for Multiexperience Development Platforms

Analyst house Gartner, Inc. recently released the 2019 version of its Magic Quadrant for Multiexperience Development Platforms. This is the first Magic Quadrant of its kind, its predecessors having been Magic Quadrants for mobile app development platforms (MADPs). This change reflects the evolution of MADPs to serve additional use case and development requirements, beyond just mobile apps. This includes the development of progressive web apps, conversational apps, immersive apps, and wearable apps.
Successful vendors in the multiexperience development platforms (MXDP) market are focused on serving the needs of devlopment teams in IT departments, and increasingly in business. Custom mobile app development will remain at the center of MXDPs, but the need to create progressive web apps and conversational apps is increasing; this includes chatbots deployed within custom mobile and web apps. AR, VR, and wearable apps will also see increased focus in the coming years.
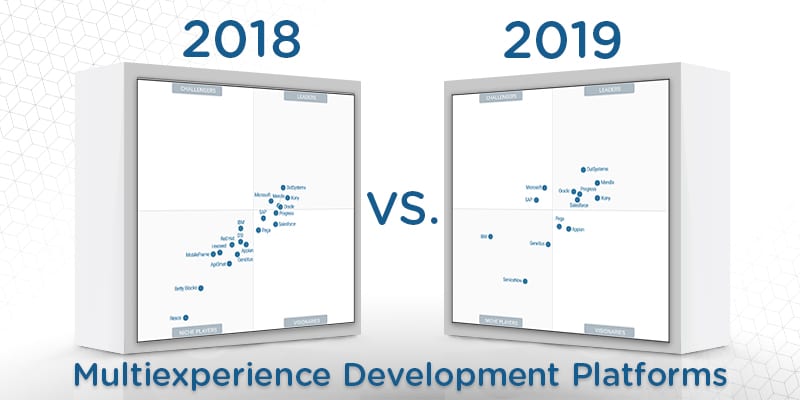
In this Magic Quadrant, Gartner evaluates the strengths and weaknesses of 13 providers that it considers the most significant in the marketplace and provides readers with a graph (the Magic Quadrant) plotting the vendors based on their ability to execute and their completeness of vision. The graph is divided into four quadrants: niche players, challengers, visionaries, and leaders. At Solutions Review, we’ve read the report, available here, and pulled out the key takeaways.
As this is the first Magic Quadrant of its type, every vendor on the map is new. This year’s inaugural members are: Appian, GeneXus, IBM, Kony, Mendix, Microsoft, Oracle, OutSystems, Pega, Progress, Salesforce, SAP, ServiceNow.
OutSystems tops this year’s Leaders quadrant by emphasizing a low-code approach to app development. The platform supports a full app life cycle and helps achieve agility using a modular architecture that has potential for heavy reuse. OutSystems’ marketing efforts have also helped it achieve a global presence and market awareness. Mendix has differentiated itself by focusing on multiexperience development productivity for citizen and professional developers, supported by a common MASA. The platform emphasizes visual- and model-driven development.
Oracle establishes its position in the Leaders quadrant by extending its mobile app and web development capabilities to native chatbots with trained AI models. The vendor’s back-end services include a deep portfolio of preexisting connectors, and offers a variety of services including location, push notifications, identity, and single sign-on. Progress’ Kinvey platform includes technologies acquired and organically built to address code-centric and low-code development. This vendor has one of the richest sets of connectors for enterprise data sources, and has strong data transformation capabilities and broad services.
Kony stands out from the Leaders quadrant with its strong track record for mobile app development, in addition to supporting smartwatch, AR, conversational apps, and progressive web apps. This vendor combines low-code with MASA best practices through the use of API management and comprehensive back-end services. Salesforce continues to invest heavily in MXDP capabilities, and its platform is well suited for a variety of personas. Customers highly praised this vendor’s roadmap to support future multiexperience needs.
Microsoft leads the Challengers category, and is close to crossing over as a Leader. This vendor has a massive developer community and ecosystem for all its MXDP products, and allows its customers to use what they need. Switching between products is very easy, and Microsoft invests significant resources into its support. SAP has introduced Backend Service Generator that provides an easy way to visually design an app or add custom app logic. SAP Cloud Platform offers a variety of low-code development options, which provides customers with different software depending on project requirements.
Pega is a Visionary in this year’s quadrant, and differentiates itself by enabling its PegaCRM Suite to be built alongside its MXDP, thereby extending all of its CRM functionality via the MXDP. This vendor allows users to design new functions or distribute parts of existing apps as microapps. Pega also offers case flows, process flows, and application-specific flows that are modeled natively in the system. Appian’s outstanding business rules, process, and decision engine capabilities make it a good choice for complex process-oriented use cases. This vendor also has a growing set of cloud security certifications, and invests in strict security requirements.
IBM is a Niche Player, and distinguishes itself in the market by providing flexible deployment options. It is also one of the few MXDP vendors that offers integrated artificial intelligence services, enabling developers to implement chatbots and machine learning models. GeneXus offers a flexible development platform that can generate code for web, mobile, wearable, and conversational apps, while ServiceNow offers custom workflow applications and is quickly gaining momentum from its customers.
Read Gartner’s Magic Quadrant.
- The 6 Best Application Development Podcasts You Should Be Listening To - February 21, 2020
- The 4 Best Application Development TED Talks for Practitioners - February 19, 2020
- The Best Application Development Events and Conferences to Attend in 2020 - February 13, 2020